Ocean Acidification Effects On Marine Life
Changes in ocean chemistry can affect the behavior of non-calcifying organisms as well. Carbon dioxide emissions are killing off coral reefs and kelp forests as heat waves and ocean acidification damage marine ecosystems scientists have warned.
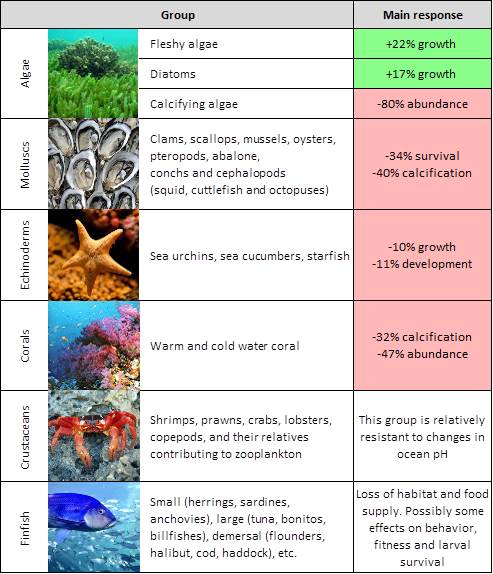 Ocean Acidification And Its Effects Coastadapt
Ocean Acidification And Its Effects Coastadapt
Some algae and seagrass may benefit from higher CO 2 concentrations in the ocean as they may increase their photosynthetic and growth rates.

Ocean acidification effects on marine life. Ocean acidification can negatively affect marine life causing organisms shells and skeletons made from calcium carbonate to dissolve. One of the most devastating impacts of rising ocean acidity could be the collapse of food webs Marine animals interact in complex food webs that may be disrupted by ocean acidification due to losses in key. Writing in Scientific Reports.
An overview of research and comparisons with other vent systems in Oceanography and Marine Biology An Annual Review Vol. Ocean acidification can cause the mass extinction of marine life fossil evidence from 66m years ago has revealed. While ocean acidification does not appear to cause direct mortality in corals several studies suggest that the survival of both major calcifying groups will be indirectly affected by ocean acidification mainly because of its effects on skeletal growth.
The more acidic the ocean the faster the shells dissolve. This effect far exceeds the individual. The effects of ocean acidification are not equal.
Carbon dioxide emissions are killing off coral reefs and kelp forests as heat waves and ocean acidification damage marine ecosystems scientists have warned. Ocean and coastal acidification puts many marine life forms at risk by affecting the ability of ocean life to build shells and skeletons stay healthy and survive during larval growth stages. Writing in Scientific Reports.
Laboratory and mesocosm experiments show that ocean acidification may affect all marine life for example through changes in gene expression physiology reproduction and behaviour 7 10. Taylor Francis 237. Ocean acidification impacts on fish and seaweeds.
Some regions and organisms will be affected to a greater degree and sooner than others. In fact the shells of some animals are already dissolving in the more acidic seawater and thats just one way that acidification may affect ocean life. Ocean acidification affects marine life Coastal and marine ecosystems are under tremendous stress from climate change.
Animals that produce calcium carbonate structures have to spend extra energy either repairing their damaged shells or thickening them to survive. However a more acidic environment will harm other marine species such as molluscs corals and some varieties of plankton Figure 4. The harmful impact of ocean and coastal acidification on marine life especially shellfish may affect the livelihood of vulnerable indigenous communities in Alaska on the West Coast and the Gulf Coast that depend on these coastal resources.
The ability of some fish like clownfish to detect predators is decreased in more acidic waters. Many coastal waters are already experiencing the negative. The impacts of ocean acidification are not uniform across all species.
While the full implications of elevated CO 2 on marine ecosystems are still being documented there is a substantial body of research showing that a combination of ocean acidification and elevated ocean temperature driven mainly by CO 2 and other greenhouse gas emissions have a compounded effect on marine life and the ocean environment. Such a relatively quick change in ocean chemistry doesnt give marine life which evolved over millions of years in an ocean with a generally stable pH much time to adapt. The carbon dioxide vents of Ischia Italy a natural system to assess impacts of ocean acidification on marine ecosystems.
Oceana acidification may cause many negative effects on a variety of marine species and ecosystems which would have rippling consequences throughout the entire ocean. Beyond respiration there is a series of coastal processes that promote acidification and high CO 2 conditions but have minor effects on DO levels including the discharge of acidified riverine water acid deposition sea ice melting and the lower alkalinity of coastal zones that results in a lower buffering capacity against acidification compared with ocean regimes. The importance of coastal resources goes beyond food to a potential loss of cultural heritage.
Overall its expected to have dramatic and mostly negative impacts on ocean. Just as carbonated soda water is more acidic than flat tap water higher levels of carbon dioxide CO2 in the ocean cause the water to become more acidic. A key impact of todays climate crisis is that seas are again getting more acidic.
Ocean acidification paired up with other climate impacts like warming waters deoxygenation melting ice and coastal erosion pose real threats to the survival of many marine species.
4 Effects Of Ocean Acidification On Marine Ecosystems Ocean Acidification A National Strategy To Meet The Challenges Of A Changing Ocean The National Academies Press
 Ocean Acidification Environmental Issues At Faculty Of International Relations
Ocean Acidification Environmental Issues At Faculty Of International Relations
 Ocean Acidification National Oceanic And Atmospheric Administration
Ocean Acidification National Oceanic And Atmospheric Administration
 Mind The Graph Blog Consequences Of Ocean Acidification On Marine Animals
Mind The Graph Blog Consequences Of Ocean Acidification On Marine Animals
 Mind The Graph Blog Consequences Of Ocean Acidification On Marine Animals
Mind The Graph Blog Consequences Of Ocean Acidification On Marine Animals
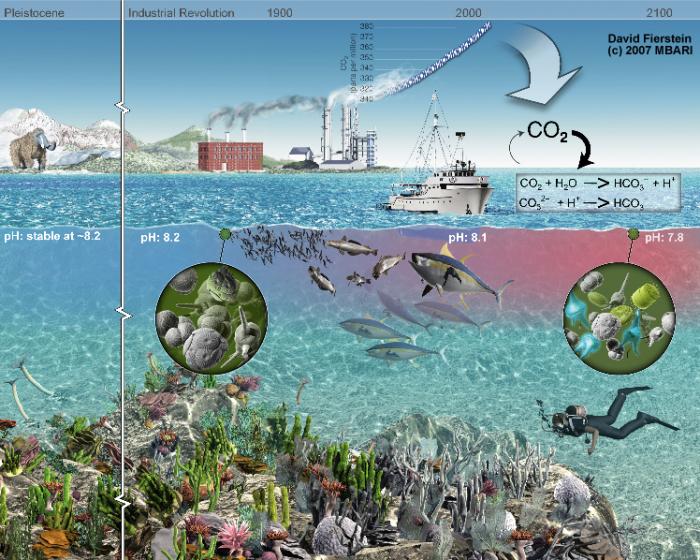 Ocean Acidification Earth 103 Earth In The Future
Ocean Acidification Earth 103 Earth In The Future
 Study Shows Ocean Acidification Is Having Major Impact On Marine Life
Study Shows Ocean Acidification Is Having Major Impact On Marine Life
 4 Effects Of Ocean Acidification On Marine Ecosystems Ocean Acidification A National Strategy To Meet The Challenges Of A Changing Ocean The National Academies Press
4 Effects Of Ocean Acidification On Marine Ecosystems Ocean Acidification A National Strategy To Meet The Challenges Of A Changing Ocean The National Academies Press
 Marine Life And Ocean Acidity Neef
Marine Life And Ocean Acidity Neef
Ocean Acidification Smithsonian Ocean
 Ppt Epa Has Taken Initial Steps To Limit Emissions That Cause Climate Change And Ocean Acidification Powerpoint Presentation Id 2016762
Ppt Epa Has Taken Initial Steps To Limit Emissions That Cause Climate Change And Ocean Acidification Powerpoint Presentation Id 2016762
 7 Harmful Effects Of Ocean Acidification On Marine Life Help Save Nature
7 Harmful Effects Of Ocean Acidification On Marine Life Help Save Nature
 Ocean Acidification Impacts On Sea Life Wxshift
Ocean Acidification Impacts On Sea Life Wxshift

Comments
Post a Comment