Coral Reef Climate
3 Responses to Do coral reefs help fight climate change The other factor not being considered is the permanency of carbon stored in the form of calcium carbonate. Threats to coral reefs.
 An Idea To Save Coral Reefs From Climate Change Takes A Step Forward The Economist
An Idea To Save Coral Reefs From Climate Change Takes A Step Forward The Economist
Scientists have discovered some deep water coral that may yield a detailed climate record of.

Coral reef climate. This Perspective considers the limited data on effects to coral reefs. According to the latest Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change IPCC Special Report climate change is making oceans warmer and more acidic and these changes are having a big impact on coral reefs. Nearly all coral reefs are projected to be lost with 2C warming by the end of the century.
In fact reef-building corals cannot tolerate waters below 64F 18C. Limiting global average temperature to well below 2C above pre-industrial levels and pursuing efforts to limit the temperature increase to 15C in line with the Paris Agreement on climate change provides the only chance for the survival of coral reefs globally. Climate change can indirectly cause harm to coral reefs too.
First coral reefs dont exist everywhere in the world. Climate change ocean change. They can only tell scientists about climate in warm tropical waters.
That process is called biomineralisation. Rising temperature and acidity make it harder for animal inhabitants to weather disease outbreaks extreme storms or. The worlds ocean is a massive sink that absorbs carbon dioxide CO 2.
However coral reefs are not only found in these areasthere are even coral reefs in the deep sea. The wet season occurs in the winter months. Anthropogenic climate change poses a serious threat to coral reefs around the world.
Climate change could destroy almost all of Earths coral reef habitats by 2100 according to new research. Coral has existed continuously for the past 40 million years surviving temperatures and carbon dioxide levels significantly higher than what is occurring today. Although this has slowed global warming it is also changing ocean chemistry.
Coral reefs are important ocean habitats and offer a compelling case of the risks of climate changeReefs provide a large fraction of Earths biodiversitythey have been called the rain forests of the seas Scientists estimate that 25 percent of all marine species live in and around coral reefs making them one of the most diverse habitats in the world. Forests though excellent stores for carbon also decompose rot andor burn more readily than a coral reef. Climate change and other human activities are decreasing ocean oxygen content.
And their survey of 2500 Indo-Pacific reefs showed that coral responses to global climate change may be changing as corals have different past experiences and tolerances to heat and stress. The weather in the coral reef is generally very sunny. Most coral reefs are found in shallow tropical or semi-tropical habitats where they enjoy warm waters and ample sunlight year-round.
Increased greenhouse gases from human activities result in climate change and ocean acidification. There is higher humidity more rainfall and warmer temperatures. The impacts of global warming can be isolated by studying long-lived corals growing on.
The reef-building corals are very sensitive to temperature fluctuations and are generally found in warm tropical and sub-tropical oceans located below 30 latitude where the annual water temperature ranges between 20-28C. It is now agreed by coral reef scientists around the world that the marine environment in general and coral reefs in particular are being adversely affected by climate change. Recent warming has allowed coral to expand their range poleward while still thriving near the equator.
A study by researchers at Rutgers University suggests that stony coral could survive climate change. Predicting the survival of corals based on how they adapted to global climate change over millions of years requires understanding among other things how they build reefs by secreting calcium carbonate. This season occurs during the summer months.
Are corals animals or plants or rocks. Coral thrive in warm water not cold water. The dry season has less humidity far less rainfall and colder temperatures.
The climate record left in coral reefs is detailed but limited.
 Climate Change What Impact On The Survival Of The World S Coral Reefs Bnp Paribas
Climate Change What Impact On The Survival Of The World S Coral Reefs Bnp Paribas
Climate Change Is Destroying Our Coral Reefs Here S How Scientists Plan To Save Them
 Latest Unesco Update Confirms Remaining Within 1 5 C Climate Target Is Critical For Survival Of World Heritage Listed Coral Reefs Icri
Latest Unesco Update Confirms Remaining Within 1 5 C Climate Target Is Critical For Survival Of World Heritage Listed Coral Reefs Icri
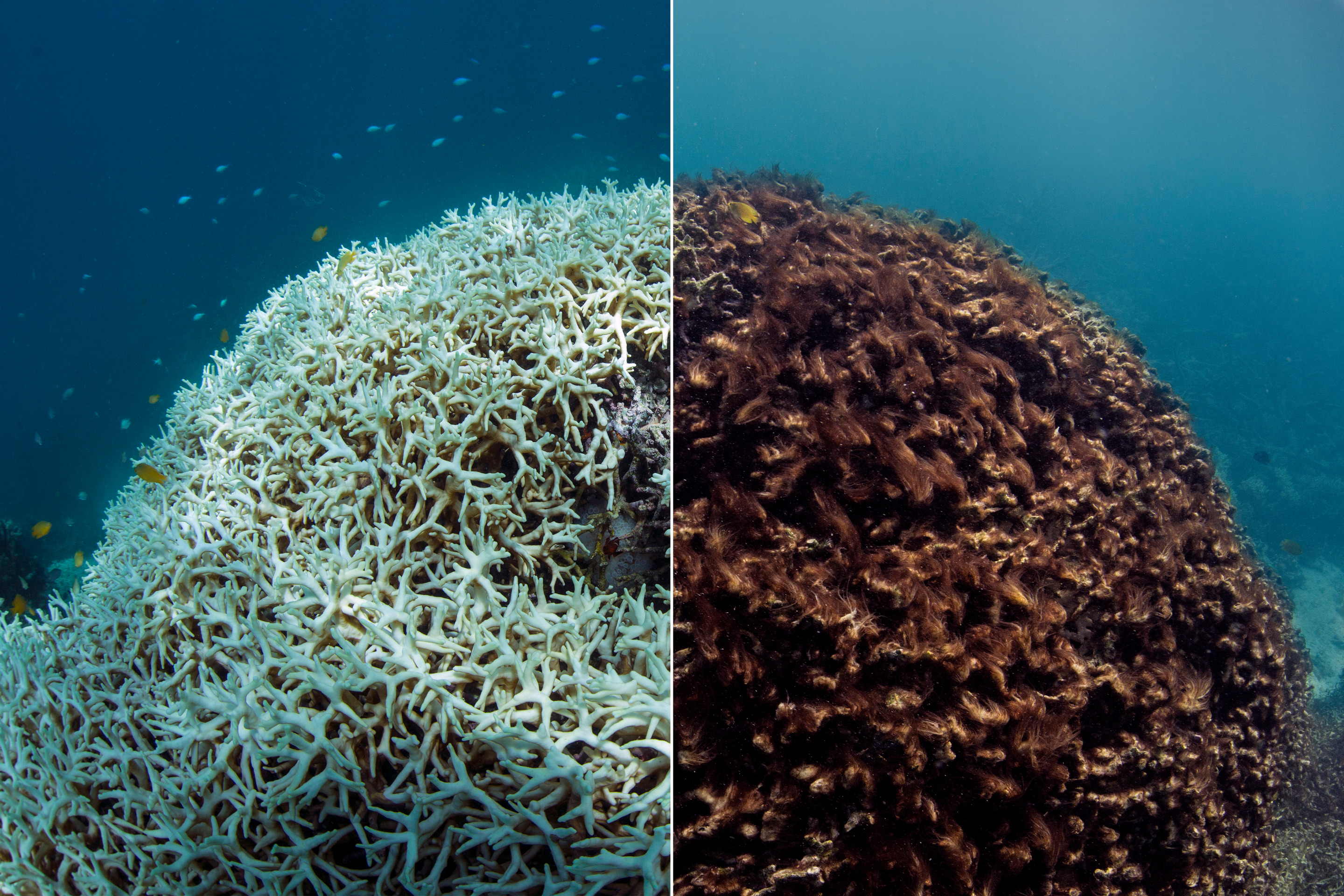 Chasing Coral Shows The Deadly Effect Of Climate Change On Our Oceans
Chasing Coral Shows The Deadly Effect Of Climate Change On Our Oceans
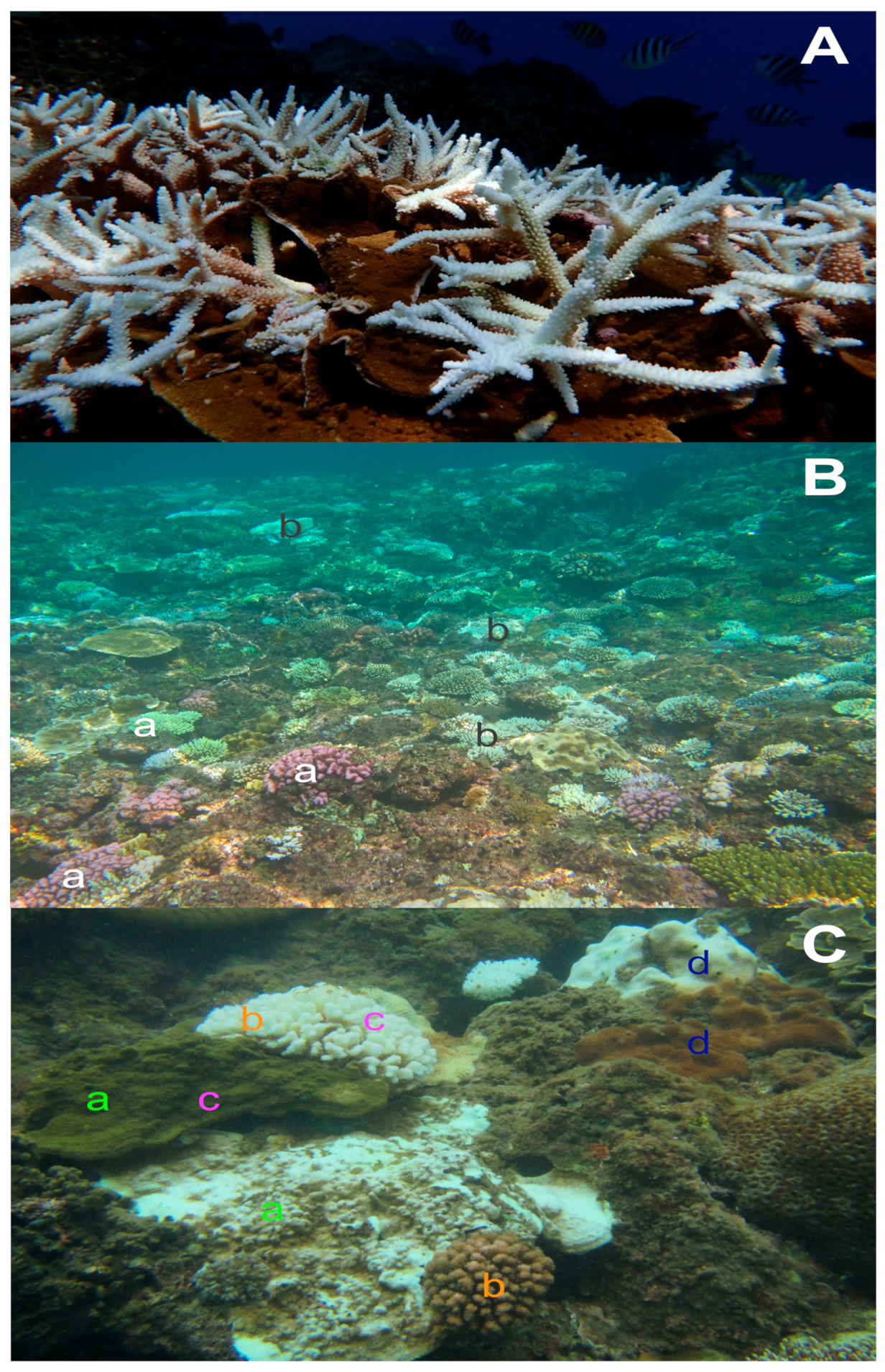 Jmse Free Full Text Thermal Stress And Resilience Of Corals In A Climate Changing World Html
Jmse Free Full Text Thermal Stress And Resilience Of Corals In A Climate Changing World Html
 Trump Administration Questions Climate Threat To Coral Reefs Mcclatchy Washington Bureau
Trump Administration Questions Climate Threat To Coral Reefs Mcclatchy Washington Bureau
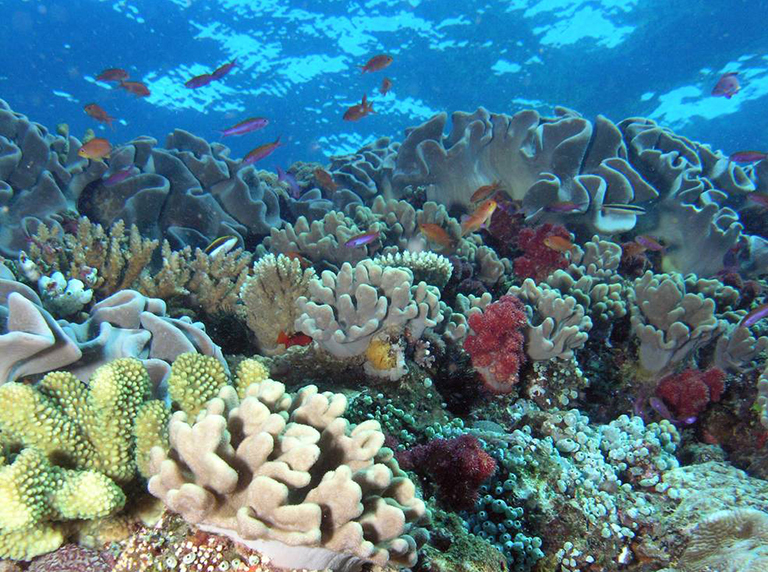 Nasa Tests Observing Capability On Hawaii S Coral Reefs Climate Change Vital Signs Of The Planet
Nasa Tests Observing Capability On Hawaii S Coral Reefs Climate Change Vital Signs Of The Planet
 How Climate Change Impacts The Great Barrier Reef Tourism Industry New Scientist
How Climate Change Impacts The Great Barrier Reef Tourism Industry New Scientist
 Coral Reefs Can Adapt To Climate Change Quiet Kinetic
Coral Reefs Can Adapt To Climate Change Quiet Kinetic
 18 Coral Reef Infographics Ideas Coral Reef Reef Coral
18 Coral Reef Infographics Ideas Coral Reef Reef Coral
 Climate Change Effects Coral Reefs By Shaianne Eastburn
Climate Change Effects Coral Reefs By Shaianne Eastburn
 How Does Climate Change Affect Coral Reefs
How Does Climate Change Affect Coral Reefs
 Study Shows That Management And Evolution Give Hope To Coral Reefs Facing The Effects Of Climate Change Uw News
Study Shows That Management And Evolution Give Hope To Coral Reefs Facing The Effects Of Climate Change Uw News

Comments
Post a Comment